Lasers Deliver More Cost-Effective, Flexible Solutions for Marking Medical Devices
Manufacturers of many types of medical devices and disposable products meet the need to mark their products by using a broad range of different laser types and machines.
June 24, 2022 by Coherent
Why do we need marking in the first place?
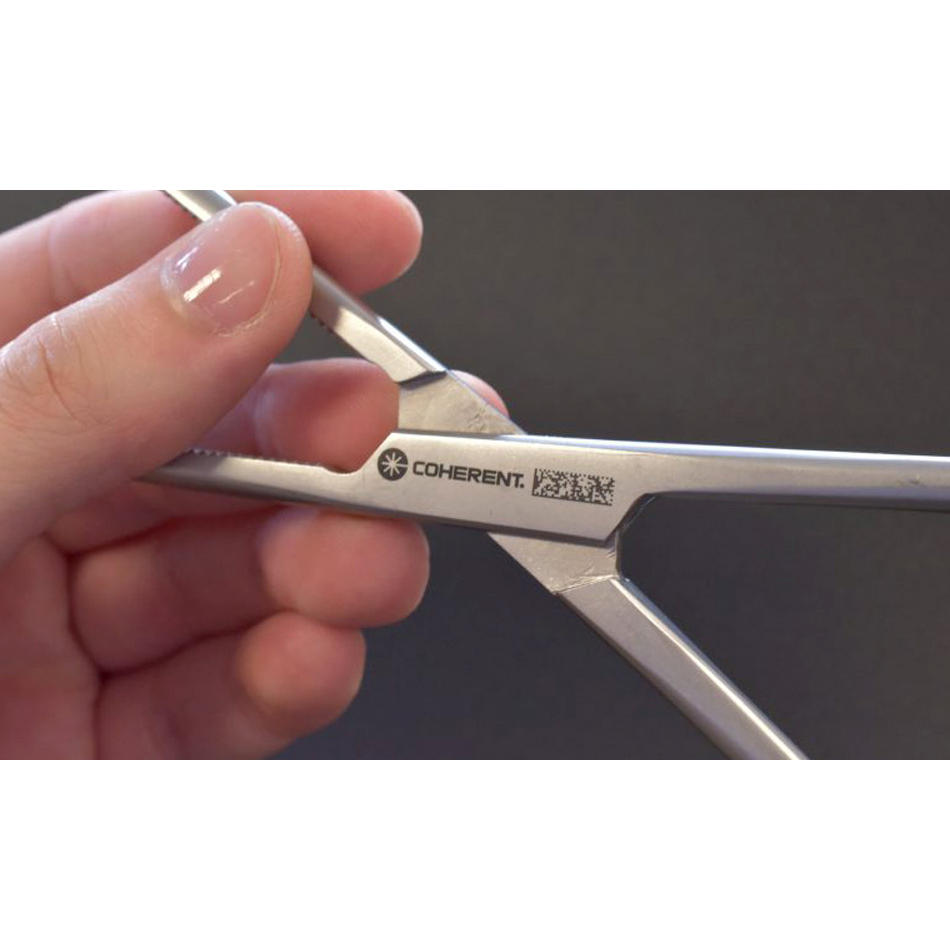
Virtually all medical devices and disposable products today have to be marked in some way, either directly or on sealed packages. Sometimes it’s to meet stringent government safety regulations as in the Unique Device Identifier (UDI) that must be permanently marked on any multi-use device like a pair of forceps. Sometimes it’s to track a batch of disposables all the way from manufacturing to actual use. Sometimes it’s for functional marks as on epi-pens or to create length gradations/fiducials on intravenous devices. And sometimes it is needed for “high value” products such as titanium implants, where sadly there is a risk of counterfeit unregulated products entering the supply chain at some point.
Why is laser marking the best solution in so many applications?
Laser marking has rapidly grown to dominate many marking applications in medical devices (and quite a few medical disposables too). That’s because laser marking provides an unmatched combination of advantages and benefits. For example, laser marking is contamination-free and uses no inks or other consumables. Consequently, it’s usually more cost-effective to implement than non-laser methods. It’s also flexible with software control, so it can easily create anything from simple letters and numbers to sophisticated symbols, graphics, and logos. Just as important, the laser creates a permanent mark that cannot be peeled away like a label, or removed with solvents like ink. And the use of laser marking is now so widespread because it can mark virtually any metal, plastic, or other material used in medical devices and disposables.
Variety is the spice of life
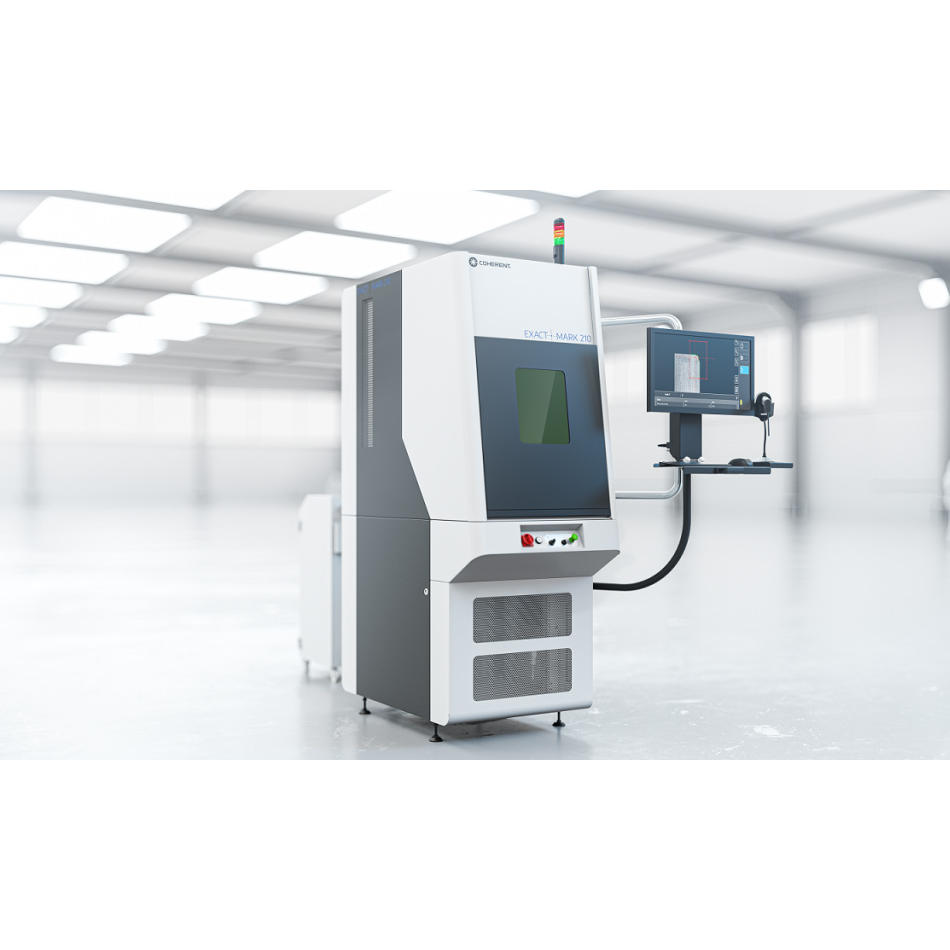
With a wide variety of both metal and plastic parts, a broad range of package types, and batch sizes ranging from 1 to tens of thousands, there’s just no way that a single laser machine type or even a single laser process type can meet all these different marking needs. That’s why Coherent offers several different optimized marking solutions, from laser marking sub-systems for simple and demanding applications to fully-automated systems (machines) like our ExactMark series that offer unattended operation on batches of identical devices often with serialization numbers. Let’s take a look at just a few of the laser marking approaches involved.
Ultraviolet (UV) marking of plastics
Plastic medical products such as catheters and intubation devices may be laser marked directly or sealed in laser marked packaging or both. Ultraviolet lasers get used a lot here because they can cause a color change within many plastic materials – black on white is the most common mark. They can do this without engraving the surface, which could otherwise cause patient irritation or act as sites to host contamination. The most common UV laser type is the nanosecond DPSS laser-like our PowerLine E QT series that are available in several of our marking machines.

Figure 1: Ultraviolet lasers can mark inside colorless plastics without affecting the outer surface which is particularly useful for medical disposables.
Marking tubular metal devices
Medical devices come in all kinds of shapes and sizes, but many have a tubular shape. So Coherent makes a fully automated laser marking machine just for this application, called AutoTube Marker. The operator places a batch of parts in the input bin and scans the data code. The machine then takes over and not only rotates and marks the parts as needed, it also scans the marked parts for user-specified pass/fail standards. And just as important, it creates a full data log for tracking and certification needs. Since it’s optimized for metal devices, AutoTube Marker comes with a choice of a traditional infrared laser or an ultrashort pulse (USP) laser such as our Rapid series which enables laser black marking.
Laser black marking
In laser black marking a USP laser causes a nanostructuring of the metal surface which then traps light; the marked surface can appear quite black but without any chemical change or oxidation. Black marking is great for both aluminum and stainless steel. And the steel stays rust-resistant even after repeated sterilization (with steam.) You can read more about laser black marking here.
3D marking
So a lot of medical devices are tubular and a few are flat, but some are neither; they can have sloping, curved, or unusually shaped surfaces that need to be marked on. For many years the only way to mark these surfaces with a laser was to resort to robotics or 5-axis CNC machines. Instead, Coherent provides a “smart” 3D marking solution that combines an extremely dynamic 3D focusing technology with novel 3D machine vision and powerful marking software called Visual Laser Marker (VLM). It visualizes the relative position of the laser and workpiece and provides an accurate preview of the marked part. The VLM software also accepts CAD design files of the workpiece, supports different 2D → 3D mapping types, and adjusts the marking process to free-form surfaces automatically.

Figure 2: Some examples of the different types of 3D marking, in this case performed with a USP laser black marker.
Ready to learn more about laser marking? Check out the full range of Coherent laser marking solutions.