MDMでフェムト秒レーザによる切断が関心を集めている理由を解説
フェムト秒レーザは、性能とコストが改善されており、小型医療機器の切断品質を高めてほしいという要望が増えていることもあって、普及が急速に進んでいます。
2022年10月18日、Coherent

Coherentのファイバーレーザ式チューブ切断機とフェムト秒レーザ式チューブ切断機のシステム収益の比較。
ファイバーレーザは、コストが比較的低く、出力がスケーラブルで、信頼性が高いといった理由から、医療機器製造業界では長年の間、切断や穴開けのアプリケーションで主流となっていました。フェムト秒レーザは、切断品質の点では明らかに優位性がありましたが、市場シェアが低い状態が長く続いていました。しかし、上図に示したCoherentチューブ切断システムの販売数から明らかなように、この状況は急速に変わりつつあります。市場シェアが急激に伸びている理由をファイバーレーザとの比較で考えてみましょう。
フェムト秒レーザ – より高性能で切断品質の高い方式
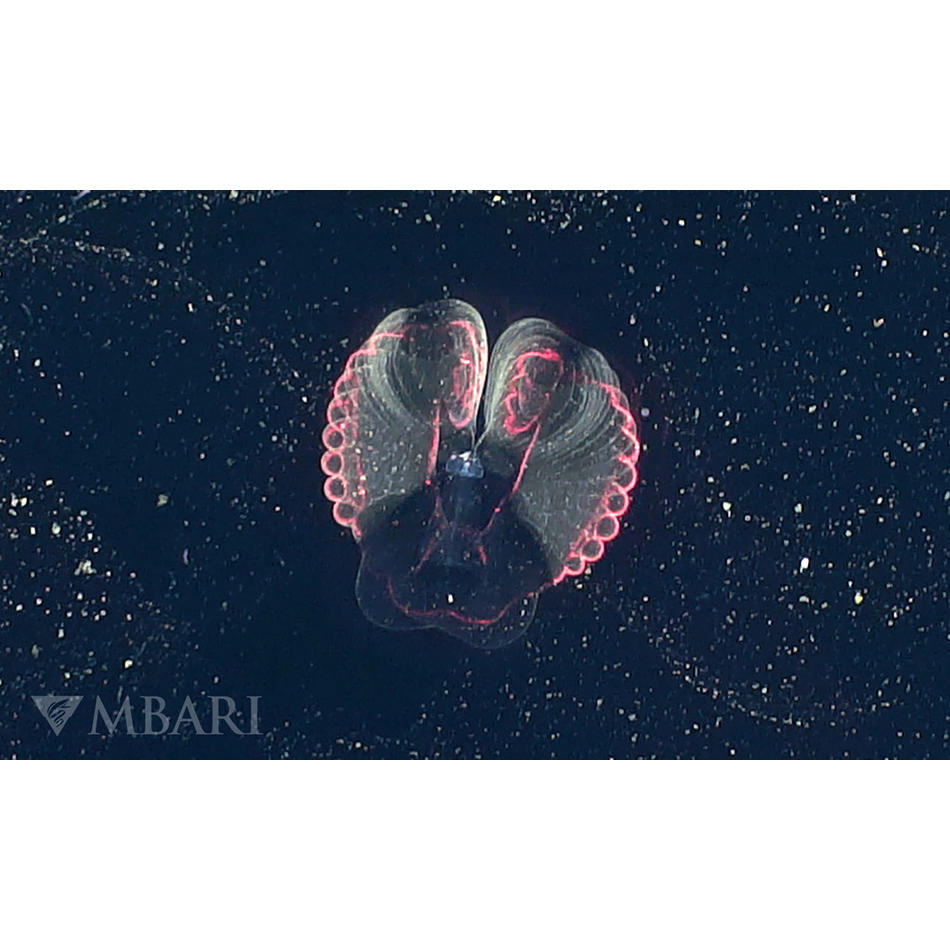
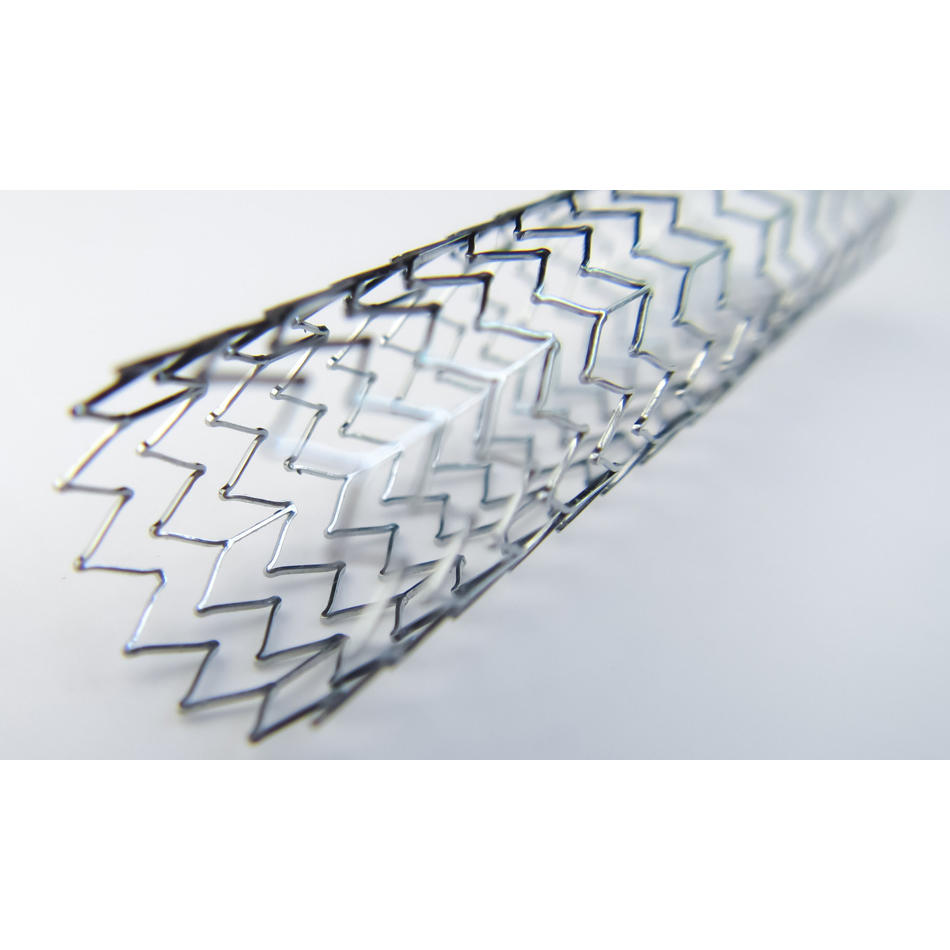
材料加工にフェムト秒(fs)レーザを使用する利点を独自に組み合わせる手法は、以前から知られていました。ファイバーのような従来のレーザでは、材料の相互作用のほとんどが光熱的なものであることから、熱影響部(HAZ)が生じます。 そのため、精密なアプリケーションでは、溶融せずにきれいに加工できる形状の最小サイズが制限され、許容できないレベルの機能的、外観的な損傷が生じることがあります。その結果、機械的な後処理(バリ取り、手動研磨、リーマ仕上げなど)がしばしば必要になります。一方、fsレーザは桁違いに短いパルスをはるかに高いピーク出力で照射するため、熱が部品に伝わる前に材料が瞬時に蒸発します。このように、より低温かつ精密な切断を行うことで、作製する形状の小型化が可能となり、再キャストの破片も生じないため、研削や研磨の必要がなくなります。さらに、この手法は、ポリマーと金属のレイヤーのような混合素材の部品など(図を参照)あらゆる材料に適用できます。

フェムト秒レーザは、ほぼすべての材料を優れたエッジ品質で切断できます。再キャスト材が発生することもありません。
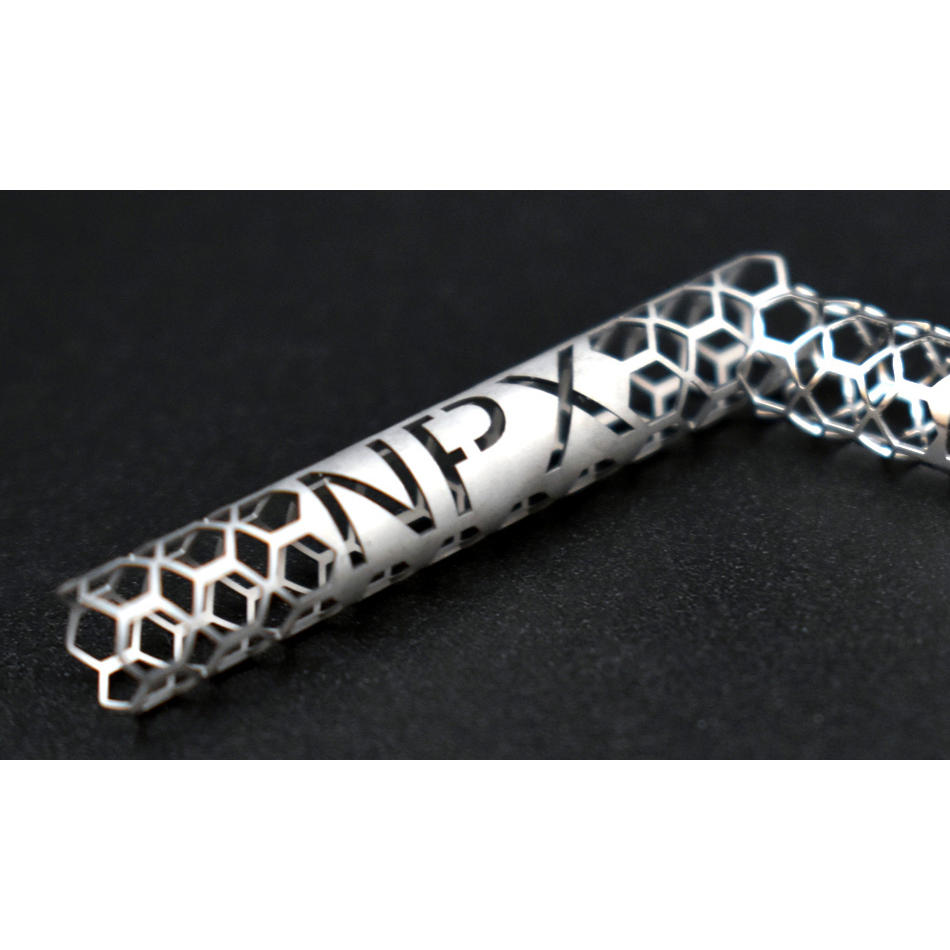
より細かな細部を持つ小型の機器(支柱など)
近年、fsレーザ加工の利用が増えている大きな要因は、小型で壁が薄く、微細な切断が多い医療機器(末梢ステント、ハイポチューブ、低侵襲ツールなど)に対する需要です。特に、上図のようなチューブ切断形状に合わせて設計された機器の需要が増えています。また、より難易度の高い材料やより高価な材料が使用されていることも、副次的な要因となっています。たとえば、マグネシウム製の生体吸収性ステントでは、ファイバーレーザを照射した後の後処理によって、歩留まりが50%に低下する場合があります。しかし、fsレーザによる切断では後処理は不要です。他の産業(ディスプレイやエレクトロニクスなど)もこの技術に移行しつつあり、市場の需要は一層増加しています。こうしたことが、各レーザメーカーが先進的なfsレーザやマシンを開発するさらなる動機となっています。
fsレーザの進化 - 出力の向上、ワットあたりのコストの削減
実際、フェムト秒レーザは、性能、経済性、信頼性の点で新たな成熟レベルに達しました。出力はスループットに直結するため、特に重要な性能パラメータです。次世代のfsレーザの例として、Coherent Monacoシリーズがあります。このシリーズは、販売チャートで示されている期間中に最大出力が20 W未満から60 W超へと連続的に上昇しています。最近では、ほとんどのフェムト秒レーザで、ワットあたりのコストも下がっています。そのため、これらのレーザは、部品あたりのコストを抑えながら、より高いスループットを得ることができます。初期のMonacoモデルは、要求の厳しい生産環境の中、24時間365日の体制で数年間稼動し続けています。これは、fsレーザの信頼性の向上が、総所有コストの削減に一層寄与していることを示しています。このことは、機械的な後処理工程の廃止によるコスト削減と相まって、いくつかの精密切断作業に経済的な転換点を間違いなくもたらしました。
効率的な自動化されたマシン
言うまでもなく、医療機器製造者のほとんどは、レーザが必要なのではなく、レーザマシン一式を必要としています。最終的には、部品の操作と検査が自動化された効率的で高性能なfsレーザマシンを利用できることが必要です。これには、幅広いトレーニングや専門知識を必要としない、使いやすいソフトウェアも含まれます。これにより、ユーザーは柔軟に小ロットのさまざまな機器をすばやく切り替えたり、大量の部品を長時間無人で処理したりできます。たとえば、CoherentのExactCutシリーズでは、当社の最新のオペレーティングソフトウェアである Coherent Laser FrameWorkが採用されています。
結論:ファイバーレーザ、fsレーザ、両方のレーザのどれを選ぶべきか?
現在、MDMに従事する人が新しいマシンを入手する際、最大の問題の一つとなるのは、fsとファイバーレーザのどちらを選択すべきかということです。ファイバーレーザに残っている主な利点は、利用できる出力が高いためより速く部品を切断できること、そしてより厚い部品を切断できることです。しかし、部品が薄くなると、多くの場合、出力と速度の利点は低下します。これは、繰り返し周波数を下げて、熱損傷の累積を避ける必要があるためです。つまり、最適なレーザの種類は、事実上アプリケーションの仕様によって決まるということです。
現在提供されている切断用医療機器向けの最新のレーザマシンで、fsレーザとファイバーレーザのいずれかを選べるのも、両方のレーザを備えたハイブリッドオプションを選べるのも、こうした理由からです。ハイブリッドオプションでは、ファイバーレーザで切断した方が経済的になる場合、あるいはfsレーザで切断した方が経済的になる場合に、単一のジョブ内でレーザをシームレスに切り替えることができます。
Coherent StarCut Tube Hybridが、Motion Dynamics社の神経サブアセンブリのレーザ切断にどのように役立ったかについての詳細をご覧ください。
関連資料